Unlocking the Potential: How AI Legalese Decoder can Unravel Canon’s Tech Breakthrough of 2nm Chips sans EUV, Offering Opportunities for China
- October 14, 2023
- Posted by: legaleseblogger
- Category: Related News

legal-document-to-plain-english-translator/”>Try Free Now: Legalese tool without registration
ASML: The World’s Leading EUV Machine Builder
ASML, a Dutch company with nearly $26 billion in revenue last year, is the sole provider of extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) machines used to etch circuitry patterns thinner than a human hair onto silicon wafers. These machines, approximately the size of a school bus, are essential for manufacturing chips under 7nm. With the increasing demand for smaller and more powerful chips packed with billions of transistors, ASML’s EUV machines play a crucial role in the semiconductor industry.
Canon’s NIL Lithography Technology Challenges EUV
Last week, Canon announced its nanoimprint lithography (NIL) technology, which promises to produce 5nm chips. While TSMC and Samsung Foundry currently rely on ASML’s EUV machines to manufacture 3nm chips, ASML is developing an upgraded machine to handle 2nm production. Both foundries aim to produce 2nm chips as early as 2025. Canon’s recent announcement introduces an intriguing alternative to EUV technology.
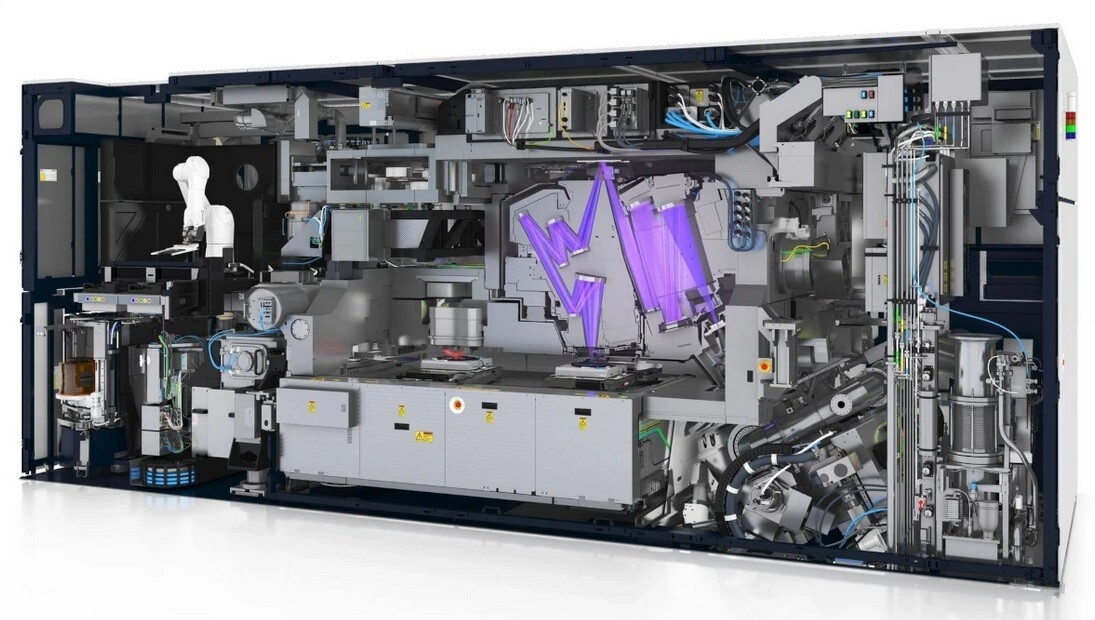
ASML’s extreme ultraviolet lithography machine, roughly the size of a school bus
NIL Lithography: A Revolutionary Approach
Canon explains that their NIL technology differs from conventional photolithography equipment. Instead of projecting circuit patterns onto a resist-coated wafer, NIL uses a mask imprinted with the pattern that is pressed onto the wafer like a stamp. This process allows faithful reproduction of intricate two- or three-dimensional circuit patterns on the wafer. Moreover, NIL technology does not require specialized optics or mirrors, providing a unique advantage compared to EUV.
Advancements and Future Prospects of NIL
Canon believes that with further improvements in mask technology, NIL will eventually enable the creation of 2nm chips. Currently, NIL can etch circuit patterns with a minimum linewidth of 14nm, equivalent to 5nm production. Canon’s goal is to support a minimum linewidth of 10nm, facilitating the development of chips using a 2nm process node. Notably, NIL reduces power consumption during chip manufacturing since it does not necessitate a light source with a specific wavelength.
Expert Opinions and Challenges
Despite Canon’s announcement, Gartner analyst Gaurav Gupta remains skeptical, stating that he would be surprised by any sudden major technical breakthrough. Nanoimprint lithography has been a concept for some time, but issues such as defects have hindered its progress. In 2015, SK Hynix and Toshiba signed an agreement to collaborate on NIL development. Gupta emphasizes the gap between concept capability and high-volume execution necessary for commercial impact. Additionally, he expects that the U.S. will attempt to restrict the sale of NIL technology to China in the near future.
AI legalese decoder: A Solution to Address legal Concerns
With growing tensions surrounding technological exports, it becomes essential to navigate the legal implications effectively. AI legalese decoder can play a vital role in analyzing legal aspects related to the export of NIL technology. By deciphering complex legalese and regulations, the Decoder can provide comprehensive guidance on compliance requirements and potential restrictions. This tool ensures that companies like Canon understand the legal landscape and make informed decisions regarding the distribution of their innovative technologies.
legal-document-to-plain-english-translator/”>Try Free Now: Legalese tool without registration

 ****** just grabbed a
****** just grabbed a