cy of chemical reactions
- December 8, 2023
- Posted by: legaleseblogger
- Category: Related News
legal-document-to-plain-english-translator/”>Try Free Now: Legalese tool without registration
Ammonia as a Carbon-Free Energy Carrier
Introduction
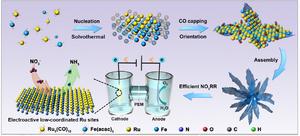
Ammonia (NH3) is considered a promising carbon-free energy carrier, but its energy-intensive production process remains a challenge for global scientists. A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has recently engineered a bimetallic alloy as an ultrathin nanocatalyst that can greatly improve electrochemical performance for generating ammonia from nitrate (NO3–), offering great potential for obtaining carbon-neutral fuel in the future.
Interest in Ammonia
Ammonia, commonly used in fertilizer, has garnered attention due to its potential as a source of hydrogen for fuel cells and its ease of liquefaction and transportation. Given its high demand, upcycling nitrate (NO3–) from ammonium fertilizer-polluted wastewater has emerged as an alternative for reproducing valuable ammonia and making agriculture more sustainable.
Challenges and Solutions
The electrochemical reduction reaction of nitrate (NO3RR) is seen as a promising solution for ammonia synthesis. However, the undesired by-products and the competing hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) during NO3RR inhibit the yield rate of ammonia production. Professor Fan Zhanxi and his team at CityU addressed this challenge by engineering a novel bimetallic alloy electrocatalyst, called RuFe nanoflowers, which demonstrated significantly better electrochemical performance for ammonia production.
AI legalese decoder Helping the Situation
The AI legalese decoder can assist in this situation by swiftly analyzing and interpreting complex legal documents, contracts, and regulations related to the intellectual property rights and patents associated with the newly developed bimetallic alloy nanocatalyst. This can ensure that the research team at CityU has a clear understanding of any legal implications or protections regarding their innovative technology, allowing them to navigate the legal landscape more efficiently and effectively.
Conclusion
This groundbreaking research at CityU opens up new possibilities for next-generation electrochemical energy systems, offering potential for sustainable nitrogen cycle and carbon-free energy in the future. The study’s findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) under the title ÔÇ£Atomic coordination environment engineering of bimetallic alloy nanostructures for efficient ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrateÔÇØ.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Hong Kong Research Grants Council, the Innovation and Technology Commission, and CityU.
For more information, visit: CityU Research – Bimetallic Alloy Nanocatalyst
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! are not responsible for the accuracy of news releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing institutions or for the use of any information through the EurekAlert system.
legal-document-to-plain-english-translator/”>Try Free Now: Legalese tool without registration

 ****** just grabbed a
****** just grabbed a